Diabetes is…
- a major cause of heart disease and stroke
- the leading cause of lower-limb amputations, kidney failure, and new cases of blindness in adults (in the U.S)
- the 7th leading cause of death in the United States
Now, you might be thinking.. that’s a lot of people! But the rate keeps increasing and it is projected that the number will double or triple for people living in the United States by 2050. Diabetes affects millions of people right now in the U. S. alone, but an additional 7 million people are undiagnosed!
What is Diabetes?
Diabetes is the name of a chronic (lifelong) disease that can be controlled but not cured. Diabetes affects the way the body uses sugar. After eating food, the body changes it to sugar and into a form of sugar called glucose. The blood stream carries this glucose to the body cells, where with the help of insulin (a hormone produced in the pancreas) it is changed into quick energy for immediate use or stored for future use. In diabetes, this normal process does not occur. With diabetes, insulin is not produced in sufficient quantities or the body is not able to use the amount that is produced. What does this really mean? This means that diabetes causes a build up of the sugar in the bloodstream which can be dangerous to our health.

Different types of diabetes:
-Type I: is controlled with insulin can be found in children and young adults; 5% of all diagnosis are type I
-Type II: is controlled through diet and exercise and used to only be found in adults, but is now found in children; 90-95% of all diagnosis are type II
-Gestational Diabetes: high blood sugar during pregnancy; usually goes away after pregnancy, but the reality is that you are 35-60% more likely to develop type II diabetes within 10—20 years if you’ve already been diagnosed with gestational diabetes
-Pre-diabetes: blood sugar levels that are higher than normal, but not in the diabetic range. There are usually no symptoms, which means that you could be part of the 7 million that are undiagnosed.
Lasting Effects of Diabetes:
Diabetes is detrimental to your health. The effects are long-lasting and permanent. As I mentioned before diabetes can cause loss of limbs, kidney failure and even blindness. The limb loss comes from your blood being unable to clot due to high levels of glucose (sugar) and so your wounds or cuts do not heal correctly making it easier for infections to occur. If the infection does not heal, your skin, tissues and bones begin to die and therefore requiring an amputation. With diabetes, the small blood vessels in the body are injured. When the blood vessels in the kidneys are injured, your kidneys cannot clean your blood properly. Your body will retain more water and salt than it should, which can result in weight gain and ankle swelling. This injury to the kidneys can ultimately lead to kidney failure.
Be informed! Know the Risk Factors!
Excessive food intake, that can cause obesity and a lack of physical activity, are the MAJOR risk factors for diabetes.
A full list of important risk factors include:
-Obesity/ lack of physical Activity
-Family history of diabetes (hereditary/predisposition)
-Race/Ethnicity: Hispanic, Native American, Pacific Islander, African American
-Older age (age 60+ years)
-History of diabetes during pregnancy
-High blood pressure (140/90 or higher)
The rates of diagnosed diabetes by race/ethnic background are: (in the U.S.)
- 7.6% of non-Hispanic whites
- 9.0% of Asian Americans
- 12.8% of Hispanics
- 13.2% of non-Hispanic blacks
- 15.9% of American Indians/Alaskan NativesThe breakdown among Hispanic adults are:
- 8.5% for Central and South Americans
- 9.3% for Cubans
- 13.9% for Mexican Americans
- 14.8% for Puerto Ricans.
If you have any of these risk factors please be aware! Some early warning signs and symptoms of diabetes include:
-frequent urination -excessive thirst -extreme hunger -unusual weight loss -increased fatigue -irritability -blurry vision or sudden vision changes -tingling or numbness in hands or feet -very dry skin -sores or wounds that do not heal -experiencing more infections than usual
If you have any of these signs and symptoms or are in any of these risk groups, you should be screened for diabetes. Early detection can lead to better and more effective treatment so that if you do develop diabetes, you can prevent blindness, amputation, heart disease, and kidney disease
Preventing and Managing Diabetes
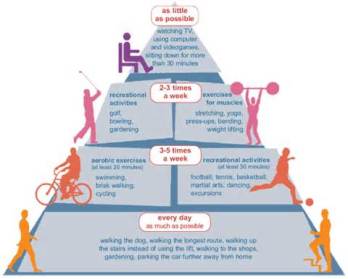
Life style changes can prevent or delay the onset of diabetes! The best way to reach and maintain a healthy life style is to participate in regular exercise, and change your eating habits. Changing your lifestyle could be a big step toward diabetes prevention or management. Its never too late to start. It’s as basic as 1, 2, and 3.
1. Get More Physical Activity
- Regular exercise can be of benefit in many ways, such as helping you lose weight and lowering your blood sugar
- Adults need at least 30 minutes a day, most days of the week
- Children need at least 60 minutes a day, preferably every day
- Pick activities the entire family can do together such as, family bike rides, dancing, hikes, etc.
- Walk up and down the soccer fields as you watch your friends and family play
2. Eat Healthy
- it’s important to eat in moderation and select a healthy variety of foods. Make your plate a healthy one.
- Cutting down sugars from your diet
- Eat more fruits and vegetables (1/2 your plate)
- These are great snack options too, instead of sugary or highly processed snacks Vegetables and fruits are also a great source of fiber that can help with digestion
- Eat whole grains instead of refined grains
- Try to eat at least 50% of your grains as whole grains
- Eat a variety of healthy proteins
- Unsalted nuts, seeds Beans, peas, soy products ,Seafood, lean meat, poultry
- Drink plenty of water
. Get Screened
- -it’s important to get screened and check your blood sugar
- Go to your doctor’s office or clinic
- If you are a college or university student, check with your health services department Dignity Health Mobile Clinic (831) 713-8751
- Low-income testing resources in the community: “Salud Para la Gente” In Watsonville (831)728-0222 In Santa Cruz (831) 423-0222 At http://www.splg.org
Diabetes…

- Es una causa mayor de enfermedades del corazón y derrame cerebrales
- Es la causa principal de amputaciones del miembro inferior, insuficiencia renal, y nuevos casos de ceguera en adultos.
- Es la séptima causa de muerte en los EE.UU.Ahora, usted podría estar pensando.. es mucha gente! Pero las cifras siguen aumentando y se proyecta que el número se duplicará o triplicará para las personas que viven en los Estados Unidos para el 2050. La diabetes afecta a millones de personas en este momento en la U. S., pero un adicional de 7 millones de personas están sin ser diagnosticados!Tomemos un momento para discutir qué es la diabetes y cuáles son los síntomas.
¿Que es la Diabetes?
La diabetes es el nombre de una enfermedad crónica (de por vida) que puede ser controlada pero no curada. La diabetes afecta la forma en que el cuerpo usa el azúcar. Después de comer, el cuerpo transforma la comida en una forma de azúcar llamada glucosa. El torrente sanguíneo transporta esta glucosa a las células del cuerpo, donde con la ayuda de la insulina (una hormona producida en el páncreas) se transforma en energía rápida para su uso inmediato o almacenada para uso futuro. En la diabetes, este proceso normal no ocurre. Con la diabetes, la insulina no se produce en cantidades suficientes o el cuerpo no es capaz de utilizar la cantidad que se produce. ¿Qué significa esto realmente? Esto significa que la diabetes provoca una acumulación de azúcar en el torrente sanguíneo que puede ser peligroso para nuestra salud.
Tipos diferentes de diabetes: 
-Tipo I: tipo común en niños y adolescentes, 5% de los diagnósticos son tipo 1
-Tipo II: solía ser encontrado en adultos solamente, pero ahora también ha sido encontrado en niños; 90% a 95% de todos los diagnósticos son tipo 2.
-Diabetes gestacional: nivel elevado de azúcar en la sangre durante el embarazo, usualmente desaparece después del embarazo; la realidad es que si ya ha sido diagnosticada con diabetes gestacional, usted es 35 a 60 mas propenso a desarrollar diabetes tipo 2 dentro de 10 a 20 años
-Pre-diabetes: niveles de azúcar en la sangre que son mas altos de lo normal, pero no en el rango diabético. Usualmente no hay síntomas, lo que significa que usted podría ser parte de las personas que aun no han sido diagnosticadas
Efectos Duraderos de la Diabetes:
La diabetes es perjudicial para su salud. Los efectos son duraderos y permanentes. Como mencioné antes, la diabetes puede causar pérdida de extremidades, insuficiencia renal e incluso ceguera. La pérdida de la extremidad viene de su sangre que es incapaz coagular debido a altos niveles de la glucosa (azúcar) y así sus heridas no se curan correctamente haciéndolo más fácil para que las infecciones ocurran. Si la infección no se cura su piel, tejidos y huesos comienzan a morir y por lo tanto requieren una amputación. Con la diabetes, los pequeños vasos sanguíneos del cuerpo están lesionados. Cuando los vasos sanguíneos de los riñones están lesionados, sus riñones no pueden limpiar su sangre correctamente. Su cuerpo retendrá más agua y sal de lo que debería, lo que puede resultar en aumento de peso y hinchazón en el tobillo. Esta lesión de los riñones puede conducir en última instancia a la insuficiencia renal.
Paso 2— ¡Infórmese y Sepa los Factores de Riesgo!
La ingesta excesiva de alimentos, que puede causar obesidad y una falta de actividad física, son los principales factores de riesgo para la diabetes. Otros factores de riesgo importantes son:
– Historia de diabetes en la familia (hereditaria / predisposición)
- – Raza: Ser Hispano, Indígena (Americano Nativo), Isleño Pacifico, Afro-Americano
- – Edad avanzada (60 años o mas de edad)
- – Historia de diabetes durante el embarazo
- – Alta presión (140/90 o mas alto)Las cifras de diabetes diagnosticada por raza / origen étnico son: (en los Estados Unidos)
- 7.6% de los blancos no hispanos
- 9.0% de los asiáticos americanos
- 12.8% de hispanos
- 13.2% de los negros no hispanos
- 15.9% de los indios americanos / nativos de AlaskaEl desglose entre adultos hispanos es:
- 8.5% para Centro y Sudamérica
- 9.3% para cubanos
- 13.9% para los mexicanos
- 14.8% para los puertorriqueños
¡Si usted tiene cualquiera de estos factores de riesgo, por favor ponga atención! Algunas de las primeras señales de advertencia incluyen:
– necesidad frecuente de orinar – sed excesiva – hambre extrema – un bajo de peso inusual – un aumento de fatiga – irritabilidad – visión borrosa o cambios repentinos en la vista – hormigueo o entumecimiento de manos o pies – piel muy reseca – llagas o heridas que no sanan – tiene mas infecciones de lo común
Si usted tiene alguno de estos signos y síntomas o está en alguno de estos grupos de riesgo, debe someterse a una prueba de detección de diabetes. La detección temprana puede conducir a un tratamiento mejor y más eficaz para que si desarrolla diabetes, puede prevenir la ceguera, la amputación, enfermedades del corazón y enfermedad renal
Ahora vamos a aprender cómo podemos prevenir y controlar la diabetes.
¡Los cambios en el estilo de vida pueden prevenir o retrasar la aparición de la diabetes! La mejor manera de alcanzar y mantener un estilo de vida saludable es participar en el ejercicio regular y cambiar sus hábitos alimenticios. Cambiar su estilo de vida podría ser un gran paso hacia la prevención o el manejo de la diabetes. Nunca es tarde para empezar. Es tan básico como 1, 2 y 3.
1. Obtenga más Actividad Física: ejercicio regular puede ser beneficioso de muchas maneras, como ayudarle
- bajar de peso y bajar el nivel de azúcar en la sangre
- Los adultos necesitan al menos 30 minutos al día, la mayoría de los días de la semana Los niños necesitan por lo menos 60 minutos al día, preferiblemente cada día
- Elija actividades que toda la familia puede hacer juntos, como paseos en bicicleta familiar, baile, caminatas, etc.
- Sube y baja los campos de fútbol mientras ves a tus amigos y familia jugar
2. Coma Saludable: es importante comer con moderación y seleccionar una variedad saludable de alimentos
- Elimine los azucares de la dieta
- Come más frutas y vegetales
- Estas son opciones de bocadillos grandes también, en lugar de bocadillos azucarados o altamente procesados, trate de agregar verduras que son de color verde oscuro, rojo y naranja
- Las verduras y frutas son también una gran fuente de fibra que puede ayudar con la digestión
- Coma granos enteros en lugar de granos refinados
- Trate de comer al menos el 50% de sus granos como granos enteros
- Coma una variedad de proteínas sanas ,Nueces sin semillas, semillas ,Frijoles,guisantes, productos de soya,Mariscos, carne magra, aves de corra
- Tome mucha agua
3. Lleve a cabo una Prueba de Detección:
- es importante hacerse la prueba de su nivel de azúcar en la sangre
- Ir a la consulta o clínica de su médico
- Si usted es un estudiante universitario o universitario, consulte con su departamento de servicios de salud
- Dignity Health Clinica Mobil (831) 713-8751
- Recursos de prueba de bajos ingresos en la comunidad: “Salud Para la Gente” En Watsonville: (831)728-0222 En Santa Cruz: (831) 423-0222 En: http://www.splg.org

 know that about 24 million people in the U.S. have diabetes?
know that about 24 million people in the U.S. have diabetes?